What is Ultimate Beneficial Ownership (UBO)?
A UBO is the individual who ultimately owns or controls an entity, directly or indirectly. Global regulations generally define a UBO as an individual who owns at least 25% of a company, though some jurisdictions, like India, have set lower thresholds (10%).
Who qualifies as a UBO?

Why Does UBO Transparency Matter?
1. Combating Money Laundering and Terrorist Financing
- Anonymous shell companies are frequently used to move illicit funds across borders
- A 2022 World Bank report found that 80% of corruption cases involved hidden UBOs
- The Pandora Papers and Panama Papers exposed how offshore structures were used to launder money
World Bank Report on Financial Crime (2022)
2. Strengthening Global Tax Compliance
- The OECD estimates that $600 billion is lost annually due to corporate tax evasion via offshore structures
- India’s Enforcement Directorate (ED) identified over ₹2,500 crore ($300 million) in offshore tax evasion through hidden UBO structures in 2023
3. Enhancing Corporate Governance and Investor Confidence
- Public UBO disclosure prevents fraud, insider trading, and politically exposed persons (PEPs) from hiding behind corporate structures
- Regulated financial markets, such as the EU, USA, and India, require investors to disclose UBO details for financial transactions and investments
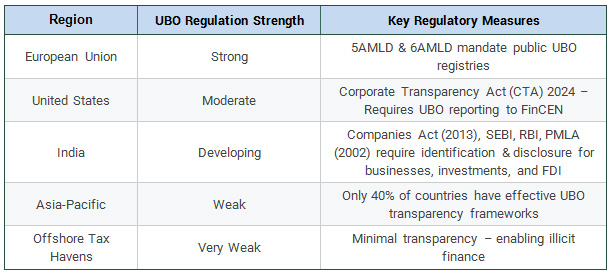
Global UBO Regulations: A Comparative Analysis
Important to understand the following:-
- How Financial Criminals Hide Ultimate Beneficial Owners (UBOs)
- Challenges in UBO Compliance
- Reporting & disclosures for UBO compliance
- Solutions for Strengthening UBO Transparency
Useful links –
- World Bank Report on Multi-Tiered Corporate Structures
https://documents1.worldbank.org/curated/en/099233504212213207/pdf/IDU001f26893087ae0443108a610078194d7562a.pdf - FATF Report on Nominee Arrangements
https://www.fatf-gafi.org/en/topics/beneficial-ownership.html
https://www.fatf-gafi.org/en/publications/Fatfrecommendations/Guidance-Beneficial-Ownership-Legal-Persons.html - OECD Report on Trusts & Foundations
https://web-archive.oecd.org/tax/transparency/index.htm - ICIJ Panama Papers Leak
https://www.icij.org/investigations/panama-papers/ - FATF Guidance on Crypto & UBO
https://www.fatf-gafi.org/content/fatf-gafi/en/publications/Fatfrecommendations/targeted-update-virtual-assets-vasps-2024.html
Full report available here: https://www.fatf-gafi.org/content/dam/fatf-gafi/recommendations/2024-Targeted-Update-VA-VASP.pdf.coredownload.inline.pdf - World Bank TBML Report
[https://openknowledge.worldbank.org/server/api/core/bitstreams/d3f6d6a4-919d-5256-bab9-b2c20494e77c/content - India’s Benami Transactions Act
- World Bank Report on Financial Crime (2022)
- OECD Global Tax Report (2024)
https://web-archive.oecd.org/tax/transparency/index.htm - EU AML Directives Dir
https://finance.ec.europa.eu/publications/anti-money-laundering-and-countering-financing-terrorism-legislative-package_en#amld6 - US Corporate Transparency Act (CTA) :
https://www.fincen.gov/news/news-releases/fincen-issues-proposed-rule-beneficial-ownership-reporting-counter-illicit - India’s SBO Rules – Companies Act, 2013
- World Bank UBO Compliance Report
- ECJ Privacy Ruling on UBOs
- India’s Financial Intelligence Unit Reports
- Blockchain & UBO Transparency Research
- RegTech & AI for UBO Compliance
- OECD CRS for UBO Data Exchange
- FinCEN UBO Compliance Penalties
