Cryptocurrencies, known for their decentralization and privacy, have emerged as a revolutionary financial tool. However, these same attributes make them attractive for illicit activities, including money laundering (ML) and terrorist financing (TF). In 2024, approximately $14.3 billion was laundered through cryptocurrencies globally, marking a significant increase due to the rise of decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms and privacy coins.
This article explores the mechanics of crypto-based money laundering, its global and regional impact, and the measures taken by regulatory bodies, including FATF recommendations and India’s regulatory response.
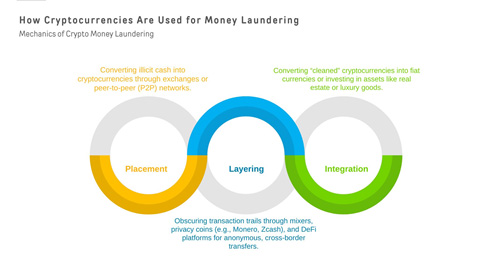
Learn more about mixing services and DeFi exploitation: Chainalysis Crypto Crime Report 2024
Impact of Cryptocurrency-Based Money Laundering
1. Financial System Risks
- Undermines trust in financial institutions
- Increases compliance costs for banks and VASPs (Virtual Asset Service Providers)
2. Criminal Exploitation
- Terrorist groups and rogue states use cryptocurrencies to evade sanctions
- Reports indicate that North Korea laundered over $1 billion in stolen cryptocurrency in 2024 to fund weapons programs
Detailed analysis of North Korea’s crypto activities:Chainalysis Crypto Crime Report 2024 [https://blog.chainalysis.com/reports/crypto-crime-2024]
3. Market Volatility
- Criminal misuse impacts legitimate market adoption and increases regulatory scrutiny
Global Regulatory Measures
1. FATF Recommendations
The Financial Action Task Force (FATF) plays a critical role in regulating cryptocurrency. Key recommendations include:
- Recommendation 15: Requires VASPs to implement AML/CFT measures
- Travel Rule: Mandates VASPs to collect and share sender/receiver details during transactions
- Risk-Based Supervision: Jurisdictions must monitor high-risk entities
- Access FATF’s full recommendations: FATF Crypto Guidelines 2024
2. U.S. and EU Regulations
- United States: Under the Bank Secrecy Act, crypto exchanges must report transactions exceeding $10,000. FinCEN Compliance Rules
- European Union: The Markets in Crypto-Assets (MiCA) regulation enforces stringent KYC norms for VASPs. European Commission – MiCA : https://commission.europa.eu/index_en
India’s Approach to Cryptocurrency Regulation
1. AML and Regulatory Framework
- Under the Prevention of Money Laundering Act (PMLA), 2002, cryptocurrency transactions are subject to AML compliance
- RBI mandates KYC verification and UBO (Ultimate Beneficial Ownership) disclosure for crypto platforms
RBI Guidelines: Reserve Bank of India Crypto Circular 2024
2. FATF Compliance
- India has adopted FATF’s Travel Rule, mandating information-sharing for crypto transfers
- FIU-India actively monitors VASP activities
FIU-India Overview: FIU-India Reports
3. Taxation Policies
- 30% tax on crypto gains and 1% TDS on transactions create audit trails, discouraging misuse
Learn more: Income Tax Department of India
Cryptocurrency offers innovation and efficiency but poses serious risks when misused for financial crimes.Regulatory bodies, including FATF, are taking proactive steps to curb crypto-based money laundering. India’s alignment with global standards, coupled with strict taxation and AML frameworks, demonstrates its commitment to combating financial crime
To secure the future of digital finance:
- Governments must harmonize regulations globally
- Financial institutions must adopt advanced compliance tools
- Continuous monitoring and evolving AML measures are essential
Additional Resources:
- FATF’s Crypto Compliance Report: FATF Official Website
- India’s Crypto Tax Guidelines: Government of India
Important to understand the following:-
- VASP regulations & Travel rule
- Implementing a Risk-Based Approaches
- Mitigation Strategies
- Regulatory framework
- Useful tools for Blockchain Analytics & investigations
